
Are you looking to maintain a healthy diet? If so, then understanding the importance of micronutrients is essential. Micronutrients, such as vitamins and minerals, play a crucial role in supporting various bodily functions, from boosting immunity to promoting proper growth and development. This article will explore how micronutrients contribute to overall well-being and provide insights into incorporating them into your everyday meals. So, whether you’re seeking to optimize your health or simply curious about how these tiny nutrients make a big impact, read on to discover the importance of micronutrients in a healthy diet.
The Basics of Micronutrients
Definition and Overview of Micronutrients
Micronutrients refer to the essential vitamins and minerals that our bodies need in small amounts to function properly. While macronutrients like carbohydrates, proteins, and fats provide the energy and building blocks for our bodies, micronutrients play a crucial role in supporting various physiological processes. They are responsible for maintaining optimal health and preventing deficiencies.
The Different Types of Micronutrients
There are two main types of micronutrients: vitamins and minerals. Vitamins are organic compounds that are required in small amounts for normal bodily functions. They are divided into two categories: fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, and K) and water-soluble vitamins (B vitamins and vitamin C).
On the other hand, minerals are inorganic elements that are essential for various physiological functions. They can be further classified into major minerals (required in larger amounts) and trace minerals (required in smaller amounts). Some examples of major minerals include calcium, magnesium, and potassium, while trace minerals include iron, zinc, and copper.
Essential Micronutrients for a Healthy Diet
Vitamin A
Vitamin A is a fat-soluble vitamin that is crucial for good vision, immune function, and cell growth. It plays a critical role in maintaining healthy skin, mucous membranes, and the integrity of our organs. Good food sources of vitamin A include carrots, sweet potatoes, spinach, and liver.
Vitamin D
Vitamin D is unique because our bodies can produce it when exposed to sunlight. It is essential for bone health as it aids in calcium absorption and promotes proper bone mineralization. Additionally, vitamin D plays a role in immune function and may have potential benefits for mood regulation. Fatty fish, fortified dairy products, and egg yolks are good dietary sources of vitamin D.
Vitamin E
Vitamin E is a powerful antioxidant that protects cells from damage caused by free radicals. It helps maintain healthy skin, immune function, and nerve function. Nuts, seeds, and vegetable oils are excellent sources of vitamin E.
Vitamin K
Vitamin K is essential for blood clotting, bone health, and proper absorption of calcium in the body. Leafy green vegetables, such as kale, spinach, and broccoli, are rich sources of vitamin K.
B Vitamins
B vitamins are a group of water-soluble vitamins that play crucial roles in energy production, brain function, and the metabolism of macronutrients. They include thiamin (B1), riboflavin (B2), niacin (B3), pantothenic acid (B5), pyridoxine (B6), biotin (B7), folate (B9), and cobalamin (B12). Whole grains, legumes, poultry, and leafy greens are excellent sources of B vitamins.
Vitamin C
Vitamin C is an essential water-soluble vitamin that acts as a potent antioxidant, supporting immune function and helping to protect against oxidative stress. It is also involved in collagen synthesis, which plays a crucial role in maintaining healthy skin and connective tissues. Citrus fruits, berries, kiwi, and bell peppers are rich sources of vitamin C.
Iron
Iron is a trace mineral that is vital for the production of red blood cells and oxygen transportation throughout the body. It plays a crucial role in energy production, brain function, and immune system support. Red meat, poultry, seafood, beans, and leafy greens are all good sources of iron.
Calcium
Calcium is a major mineral that is essential for maintaining healthy bones and teeth. It also plays a role in muscle function, nerve transmission, and blood clotting. Dairy products, leafy greens, and fortified non-dairy alternatives are excellent sources of calcium.
Magnesium
Magnesium is another major mineral that is involved in over 300 enzymatic reactions in the body. It plays a critical role in energy production, protein synthesis, muscle and nerve function, and maintaining a healthy heartbeat. Nuts, seeds, legumes, and whole grains are good dietary sources of magnesium.
Zinc
Zinc is a trace mineral that is involved in numerous physiological processes, including immune function, DNA synthesis, and wound healing. It also plays a role in taste perception and supports normal growth and development. Seafood, beef, poultry, legumes, and seeds are good sources of zinc.

This image is property of images.livemint.com.
The Roles Micronutrients Play in the Body
Enhancing Immune System Function
Micronutrients, particularly vitamins A, C, D, and E, play an essential role in supporting a healthy immune system. They help protect against infections, promote the production of immune cells, and regulate immune responses.
Supporting Brain Health and Cognitive Function
Certain micronutrients, including B vitamins, vitamin E, and omega-3 fatty acids, are crucial for maintaining optimal brain health and cognitive function. They support neurotransmitter synthesis, enhance memory and learning, and protect against age-related cognitive decline.
Promoting Healthy Vision and Eye Function
Vitamins A, C, E, and zinc are important for maintaining healthy vision and preventing eye diseases. Vitamin A is particularly important for night vision, while vitamin C and E help protect the eyes from oxidative damage caused by exposure to sunlight and other environmental factors.
Maintaining Healthy Bones and Teeth
Calcium, vitamin D, magnesium, and vitamin K are key micronutrients for maintaining strong and healthy bones and teeth. They aid in the absorption and utilization of calcium and other minerals, promoting proper bone mineralization and reducing the risk of osteoporosis and dental issues.
Regulating Energy Levels and Metabolism
B vitamins, magnesium, and iron are involved in energy production and metabolism. They help convert food into usable energy, support the breakdown of macronutrients, and ensure proper functioning of the mitochondria, the energy powerhouses of our cells.
Aiding in Red Blood Cell Production
Iron, vitamin B12, and folate are essential for the production of red blood cells, which carry oxygen to all parts of the body. Deficiencies in these micronutrients can lead to anemia, resulting in fatigue, weakness, and poor oxygen transport.
Supporting Skin Health and Wound Healing
Micronutrients such as vitamin C, vitamin E, zinc, and copper play a crucial role in maintaining healthy skin and promoting efficient wound healing. They support collagen synthesis, fight oxidative stress, and assist in the regeneration of skin cells.
Contributing to Muscle Function and Recovery
Magnesium, calcium, potassium, and B vitamins are vital for proper muscle function, including muscle contraction and relaxation. They also aid in muscle recovery and preventing muscle cramps and spasms.
Assisting in Hormone Production and Regulation
Certain micronutrients, such as iodine, iron, zinc, and vitamins A and D, are necessary for the synthesis, production, and regulation of hormones. They help support proper hormone balance and function, influencing various physiological processes in the body.
Protecting Against Oxidative Stress and Cellular Damage
Several micronutrients, including vitamins C and E, beta-carotene, selenium, and zinc, act as antioxidants, neutralizing harmful free radicals and protecting cells from oxidative damage. This helps reduce the risk of chronic diseases, including heart disease, cancer, and neurodegenerative disorders.
Micronutrient Deficiencies and Health Consequences
Common Micronutrient Deficiencies
Micronutrient deficiencies are widespread globally, affecting both developing and developed countries. Some of the most common deficiencies include iron, vitamin D, iodine, vitamin B12, and folate deficiencies.
Symptoms and Effects of Micronutrient Deficiencies
Micronutrient deficiencies can lead to a wide range of symptoms and health consequences. For example, iron deficiency can cause fatigue, weakness, and impaired cognitive function. Vitamin D deficiency can result in weakened bones, increased risk of infections, and mood disorders. Folate deficiency during pregnancy can lead to neural tube defects in the developing fetus.
Long-term Health Consequences of Micronutrient Deficiencies
Persistent micronutrient deficiencies can have serious long-term health consequences. For instance, iron deficiency anemia can impair physical and cognitive development in children. Vitamin D deficiency can increase the risk of osteoporosis, cardiovascular diseases, and autoimmune disorders. Folate deficiency during pregnancy can lead to severe birth defects.
This image is property of cdn.buttercms.com.
Achieving a Balanced Micronutrient Intake
Importance of a Varied Diet
To ensure an adequate intake of all micronutrients, it is important to consume a varied and balanced diet. Eating a wide range of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats can help provide the necessary vitamins and minerals the body needs.
Food Sources Rich in Micronutrients
Including nutrient-dense foods in your diet can help ensure sufficient intake of micronutrients. For example, fruits and vegetables are excellent sources of vitamins A, C, and K, while dairy products and leafy greens are rich in calcium. Whole grains, legumes, and lean meats provide a good balance of B vitamins and minerals.
Factors Affecting Micronutrient Absorption
Several factors can affect the absorption and utilization of micronutrients in the body. For example, certain medications, chronic diseases, gastrointestinal disorders, and aging can impair the absorption and utilization of certain vitamins and minerals. Consuming a diverse diet and addressing any underlying health conditions can help enhance nutrient absorption.
Supplementation and Fortification
In some cases, it may be necessary to supplement the diet with micronutrients to ensure optimal intake. This is especially important for individuals with specific dietary restrictions or health conditions that may result in nutrient deficiencies. Fortified foods, such as cereals and plant-based milks, can also help bridge the nutrient gap for those who may have limited access to a variety of foods.
Understanding Recommended Daily Intakes
Recommended Daily Intake Guidelines
Recommended Daily Intakes (RDIs) or Dietary Reference Intakes (DRIs) are guidelines established by health authorities to provide guidance on the recommended amounts of various nutrients needed to maintain good health. These guidelines take into account different age groups, genders, and life stages.
Factors Influencing Micronutrient Requirements
Micronutrient requirements can vary depending on several factors, including age, gender, activity level, and physiological conditions such as pregnancy or lactation. For example, pregnant women typically require higher amounts of folate and iron to support fetal development.
Special Considerations for Different Age Groups and Life Stages
Certain age groups and life stages may have specific micronutrient needs. For instance, infants and young children may require higher amounts of certain vitamins and minerals to support growth and development. Older adults may have increased requirements for certain nutrients due to age-related changes.
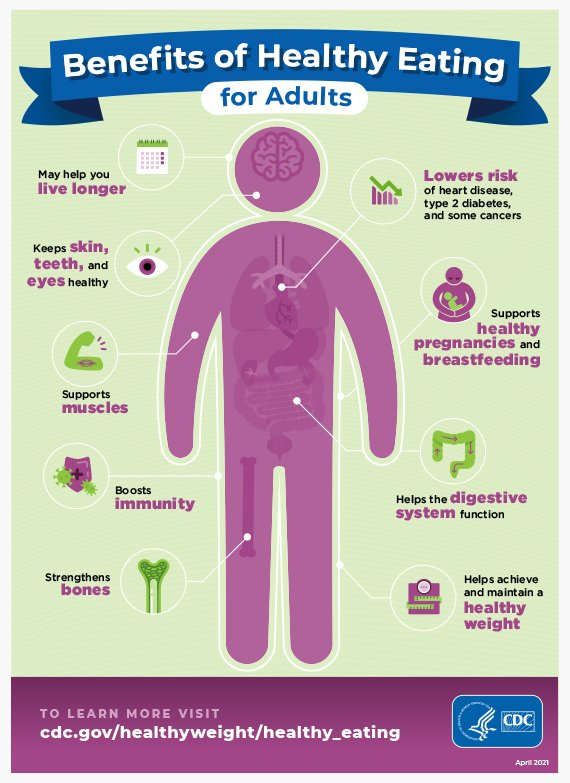
This image is property of www.cdc.gov.
Conclusion
Micronutrients are essential for maintaining good health and preventing nutrient deficiencies. They play vital roles in supporting various physiological processes such as immune function, brain health, vision, bone strength, and energy production. A balanced and varied diet that includes a wide range of nutrient-dense foods is crucial for ensuring adequate intake of all micronutrients. By understanding the importance of micronutrients and making informed dietary choices, you can optimize your health and well-being.
